Elevators, now almost necessary in most modern structures, provide ease of movement and physiologically assisted indoor transport, particularly for multi-story houses. Determining an elevator’s rating, which determines its actual capacity, is essential in the design process. This blog explores how to calculate lift capacity, factors affecting it, safety considerations, and the importance of regular maintenance.
Overview of Elevator Capacity
Elevator capacity is defined as the limit of the weight and the number of passengers the elevator can transport. This type of metric is also primary, as it defines elevators’ characteristics and requirements for their construction and performance. Proper calculation ensures the lift can handle expected traffic without compromising safety or performance.
Importance of Calculating Elevator Capacity
The following essential considerations determine an elevator’s capacity. First, check the safety of the passengers by avoiding overcrowding, which may cause mechanical breakdowns or accidents. Second, the general elevator design and structural aspects of construction to be observed in the building must be determined. Accurate capacity calculation helps select the appropriate lift model and avoid unnecessary expenses.
Factors Affecting Elevator Capacity
Several factors influence elevator capacity, including standard sizes, weight limits, and usage patterns. Understanding these variables is essential for accurate calculations.
Standard Sizes and Variations
Elevators come in various sizes, each with specific capacity ranges. Standard domestic lifts typically have a capacity between 300 to 450 kg, accommodating 3 to 6 people. However, variations exist based on design preferences and specific needs. For instance, larger domestic lifts may support up to 1000 kg, suitable for wheelchair access or carrying heavy loads.
Importance of Adhering to Manufacturer-Specified Weight Limits
Manufacturers come up with weight limits regarding their elevator models, given the mechanical and structural offer that the lift contains. It is paramount to follow the above specifications to guarantee the safety of the structure and its sustainability. Going beyond the recommended weight limit stresses every part of the elevator. It will likely develop a breakdown problem and frequent maintenance, escalating the maintenance expenses.

Calculating Elevator Capacity
To calculate elevator capacity accurately, follow these steps:
Measuring the Internal Dimensions
First, it is necessary to measure the home lift dimension. This includes the width, depth, and height of the space utilized in or needed for the building. These measurements aid in calculating the size of the car in terms of its volume, which in turn informs its carrying capacity as far as passengers are concerned.
Adjusting Capacity Based on Typical Usage Patterns
Next, consider the typical usage patterns. For residential elevators, the average weight per person is approximately 68 kg. To calculate the capacity, divide the total weight limit by the average weight per person. For example, if the elevator’s weight limit is 408 kg, the capacity would be six people (408 kg / 68 kg per person).
Adjust the capacity if the elevator will frequently carry heavy items or accommodate wheelchairs. In such cases, reducing the number of passengers is prudent to avoid exceeding the weight limit.
Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount in elevator design and operation. Ensuring compliance with safety standards and incorporating reliable protection systems are essential steps. Every building where elevators are to be installed has some requirements regarding building codes for elevators and safety standards. These are set to safeguard passengers and guarantee that the elevator is running efficiently. It encompasses issues related to weights and measures, frequent inspection, and record keeping.
Types of Overload Protection Systems
Domestic lifts are equipped with overload protection systems to prevent accidents. These systems detect when the elevator exceeds its weight capacity and take corrective action, such as preventing the elevator from moving or issuing an alarm. Common overload protection systems include load weighing devices and sensors integrated into the lift’s control system.
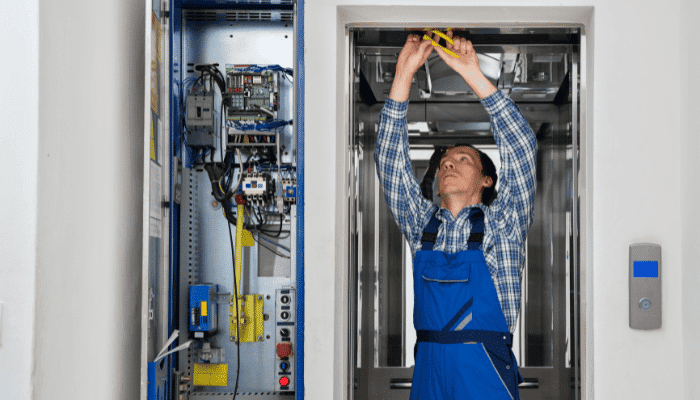

Maintenance and Inspection Requirements
Regular maintenance and inspections are vital to ensure elevators remain safe and functional. Neglecting these aspects can lead to malfunctions, increased wear and tear, and safety hazards.
Regular Maintenance Schedules
The regular maintenance schedule aims to prevent such problems before they become major ones. Routine tasks include examining mechanical parts, greasing sliding parts, and installing and inspecting electrical systems and safety devices. Maintenance of lifts used in domestic areas should be done at least twice a year.
Transform Your Living Space with SWIFT Lifts
A lift is much more than a mere convenience. SWIFT Lifts deals with supplying high-quality domestic lifts to meet clients’ needs and wants. Our lifts offer the best aesthetics and pounds and are built to be safe, efficient, comfortable, and desirable.
Whether you need to elevate your home to create a comfortable environment for elderly parents who can no longer navigate stairs or other floors or just upgrade the home’s aesthetics with quality and elegant home lifts, Swift Lifts has the perfect solution. Request a quote to learn more about our domestic lifts and which suits your home best.
FAQs
Measure the elevator car’s internal width, depth, and height to calculate its volume. These dimensions help determine the usable space and the number of passengers it can safely accommodate.
Most commercial elevators have a standard weight limit between 1,000 to 2,500 kilograms, accommodating 13 to 33 passengers. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for exact limits.
Elevator capacity should be re-evaluated annually during routine maintenance checks or whenever significant changes are made to the building’s usage or elevator system.
Exceeding the recommended capacity can strain the elevator’s mechanical components, leading to breakdowns, increased maintenance costs, and potential safety hazards like sudden stops or system failures.
Ensure compliance by consulting with professional elevator inspectors, adhering to manufacturer guidelines, and conducting regular maintenance and safety checks as required by local building codes and regulations.
Get in Touch!