How Do Elevators Work - What Types Are There?
Elevators are essential for vertical transportation, providing safe, efficient, and convenient movement between floors. Different buildings and purposes require different types of elevators, from compact home lifts to high-speed, high-capacity systems for commercial towers. Understanding how elevators work and the elevator system types helps in choosing the right solution for your space and needs.
How Do Elevators Work?
At their core, elevators move a cabin up and down using mechanical, electrical, or pneumatic systems. Most elevators consist of:
- Cabin/Platform: The part that carries passengers or goods.
- Drive System: Determines motion—common drives include screw and nut, hydraulic, traction, or pneumatic systems.
- Control System: Ensures smooth acceleration, deceleration, and safe operation.
- Safety Mechanisms: Includes emergency stops, interlocks, Anti-Trap features, and backup systems.
Some elevators, like conventional traction elevators, use counterweights and cables, while modern home elevators like SWIFT combine platform lift simplicity with advanced design and safety.
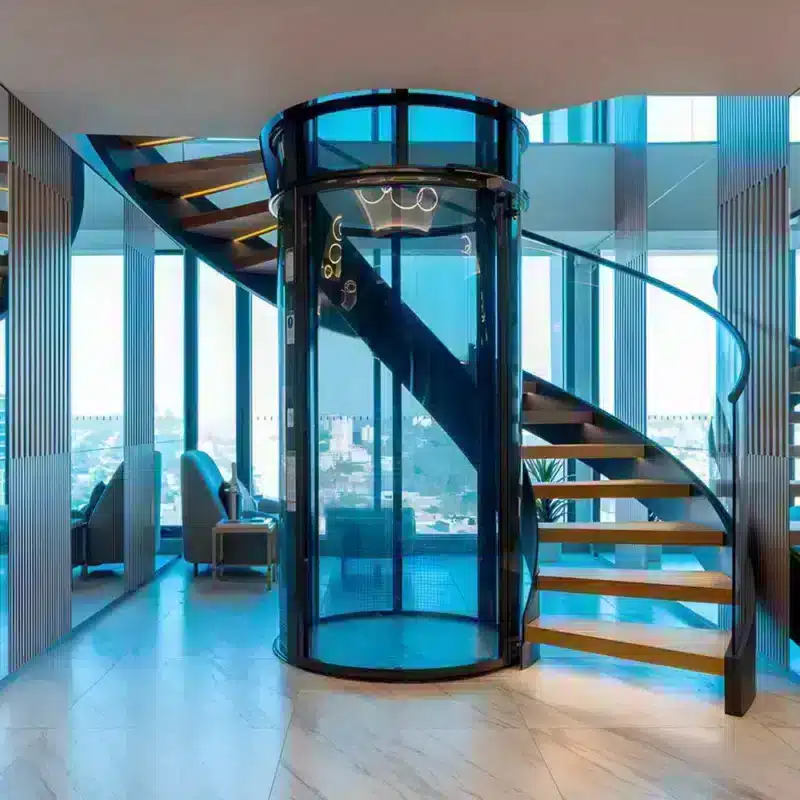

Elevator Systems Overview
| Type of Elevator | Drive System | Typical Use | Key Features |
| Conventional Elevator | Traction (cable) or hydraulic | Hotels, airports, commercial buildings | High speed, high capacity, requires shaft & pit |
| Platform Lift | Screw & nut, hydraulic | Public buildings, accessibility | Simple, robust, designed for mobility |
| Accessibility Elevator | Pneumatic, vacuum, chair lift | Elderly/disabled homes | Compact, low cost, focused on accessibility |
| Home Elevator (SWIFT) | Screw & nut | Residential homes | Safe, stylish, customizable, pitless or shallow pit |
Main Types of Elevators
1. Conventional Elevators
- Powered by belts, ropes, hydraulic pistons, or counterweights.
- Commonly used in multi-story hotels, airports, and commercial buildings.
- Require a dedicated elevator shaft, safety pit, and overhead space for the machine room.
- High-speed and high-capacity elevators suitable for thousands of passengers daily.
- Not usually practical for private homes due to space and construction requirements.
2. Platform Lifts
- Simple lifts for accessibility, often screw and nut-driven or hydraulic.
- Designed for public spaces such as museums, schools, and train stations.
- Focused on mobility support for disabled people, strollers, or small goods.
- Robust design to withstand outdoor or high-use conditions.
3. Elevators for Elderly and Disabled
- Includes chair lifts, stair lifts, hole-through-floor lifts, pneumatic and vacuum elevators.
- Focused on accessibility and cost-efficiency.
- Often compact but not always aesthetically integrated into modern living spaces.
4. Home Elevators (e.g., SWIFT)
- Designed for comfort, safety, and elegant interiors.
- Combines platform lift functionality with the beauty of conventional elevators.
- Modular shafts can be customized with glass or decorative panels.
- Can be installed directly on the floor or in a shallow 50 mm elevator pit.
- Drive system typically uses screw and nut technology, offering smooth, safe, and energy-efficient operation.
Conclusion
Choosing the right elevator system depends on your building type, space, and usage. While conventional elevators are ideal for commercial towers, home elevators like SWIFT provide a perfect balance of safety, elegance, and efficiency for modern homes. Whether renovating or building a new home, understanding all types of elevators and their operation ensures you make an informed choice.
For more details on how SWIFT elevators work, explore the full guide on screw and nut technology and platform lift solutions.