What Drive Motor Does SWIFT Use?
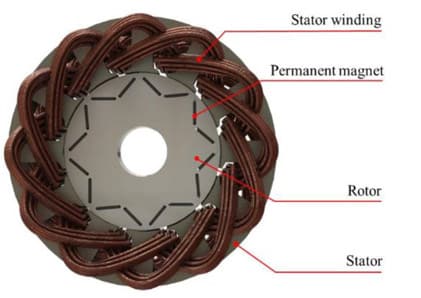
When choosing a lift for your home, one of the most important considerations is the elevator motor. The motor defines not only how efficiently the lift runs but also its smoothness, reliability, and long-term energy costs. SWIFT sets itself apart by using the same motor technology as leading EV manufacturers like Tesla – the IPM (Interior Permanent Magnet) SynRM (Synchronous Reluctance Motor). This motor is far more advanced than conventional options and offers unmatched efficiency, control, and performance.
SWIFT’s Advanced Elevator Motor Technology
- Motor Type: IPM SynRM (Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Reluctance Motor)
- How It Works: Permanent magnets are embedded inside the rotor, creating a strong magnetic field that interacts with the stator to produce motion.
Why It Matters: This design delivers better efficiency and control compared to a traditional induction motor.
Key Differences from Conventional Elevator Motors
- Construction and Design
- A conventional induction motor relies only on electromagnetic induction, with no permanent magnets in the rotor.
- The IPM SynRM motor uses permanent magnets, enabling higher performance and reduced energy loss.
- Higher Efficiency
- Performs exceptionally well at partial loads and low speeds.
- Leads to lower operating costs and better sustainability.
- Better Performance
- Provides higher torque density and smoother movement.
- Ensures precise speed control for a more comfortable ride.
- More Advanced Control
- Requires sophisticated methods like field-oriented control (FOC) for speed and torque.
- In SWIFT, this is managed by a custom-built motor controller, designed to deliver maximum efficiency.
Elevator Motor Specifications in SWIFT
- SWIFT Motor + Controller + Battery Pack work together for enhanced performance:
- Smooth acceleration and deceleration for precise landings.
- Adjustable speed via the touch display.
- Weight calculation of passengers or baggage through motor management.
- Regenerative braking that feeds energy back into the batteries – “every 4th trip for free.”
- Battery backup ensures full operation even during power failure (Anti-Trap feature).
- One-phase power operation with less peak power demand, making installation easier.
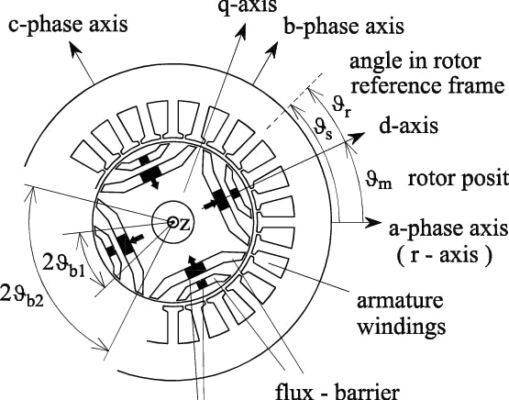
Types of Elevator Motors Commonly Used
While SWIFT relies on the IPM SynRM motor, other lifts use different motor types. Understanding these helps homeowners choose wisely:
- Elevator DC Motor
- Traditional design used in older lifts.
- Offers good torque but requires frequent maintenance.
- Elevator Traction Motor
- Widely used in commercial and residential buildings.
- Can be geared or gearless, with gearless models offering better performance.
- Gearless Traction Elevator Motor
- Provides higher speeds, smoother rides, and greater energy efficiency.
- Often used in high-rise buildings where performance is critical.
- Hydraulic Motors
- Used in some residential lifts but slower and less energy-efficient.
- Require more space for oil tanks and equipment.
What Motor Should Be Used in a Lift?
- For skyscrapers or high-rise offices, a gearless traction elevator motor is often the best choice due to speed and heavy-duty performance.
- For homes and low-rise buildings, an IPM SynRM motor like the one used in SWIFT is ideal. It balances energy efficiency, compact design, and smooth operation.
Final Takeaway
The heart of every lift is its elevator motor. While traditional options like elevator dc motors or traction motors have their place, SWIFT’s IPM SynRM motor stands out for its innovation. Combined with a custom motor controller and battery pack, it delivers smooth travel, energy efficiency, and reliability for modern homes.